Agricultural Cooperatives
|
Agricultural Cooperatives
|
|---|
Agricultural cooperatives are established to enable farmer members to engaging in business together, thus helping one another in times of crisis as well as gaining for themselves a better livelihood and quality of life.
A small credit cooperative named Wat Chan Agricultural Cooperative Unlimited Liability established at Muang district, Phitsanulok province on 26 February 1916 was the first agricultural cooperative in the country. From then on, the number of small credit cooperatives had steadily increased until the promulgation of the Cooperative Act,B.E.2511. Several of these small cooperative then grouped together, forming agricultural cooperatives at the district level. Larger and stronger cooperatives are, then, expected to provide a wider scope of services to members.
Objective of Agricultural cooperatives are generally formed to meet the members’ needs as follows:
1. To provide loans to members for productive and providential purposes at affordable interest rates;
2. To encourage members’ thrift through savings and deposits; To provide agricultural products and daily necessities for sale to members at reasonable prices;
3. To promote appropriate farm practices and disseminate technical know-how aimed to help members reduce production costs and obtain higher yields. With government assistance, members are introduced to proper cropping techniques. Another service is in the form of farm equipment (e.g., tractors. Water pumps, etc.) made available to members at reasonable charge; and To enable members to market products together, thereby obtaining higher prices for their produce and maintaining fairness in terms of weights and measures. Cooperative Operation
Organizational structure of cooperatives in the agricultural sector.
Agricultural cooperatives in Thailand are vertically organized in a three-tier system; primary cooperative at district level, provincial federation at provincial level, and national federation at national level. The primary cooperatives consist of individual members while members of provincial and national federations are cooperatives. At the provincial level, five or more primary cooperatives can together form a provincial federation which undertakes joint activities on behalf of their primary affiliates such as processing and trading of agricultural produce.
At the national level, there is the Agricultural Cooperative Federation of Thailand (ACFT) of which all provincial agricultural cooperative federations are affiliates. Note that there are also other national federations formed by specific types of agricultural cooperatives such as the Sugarcane Growers Cooperative Federation of Thailand, Swine Raiser Cooperative Federation of Thailand, Dairy Cooperative Federation of Thailand, and Onion Growers' Cooperative Federation of Thailand.
All types of cooperatives at all levels in Thailand are affiliated to the Cooperative League of Thailand (CLT), the top national apex organization which was established in 1968. The CLT is not involved in any business but operates as a cooperative education promoter of the country. Cooperatives have to pay 5% of their profit to CLT, as a fee for services.
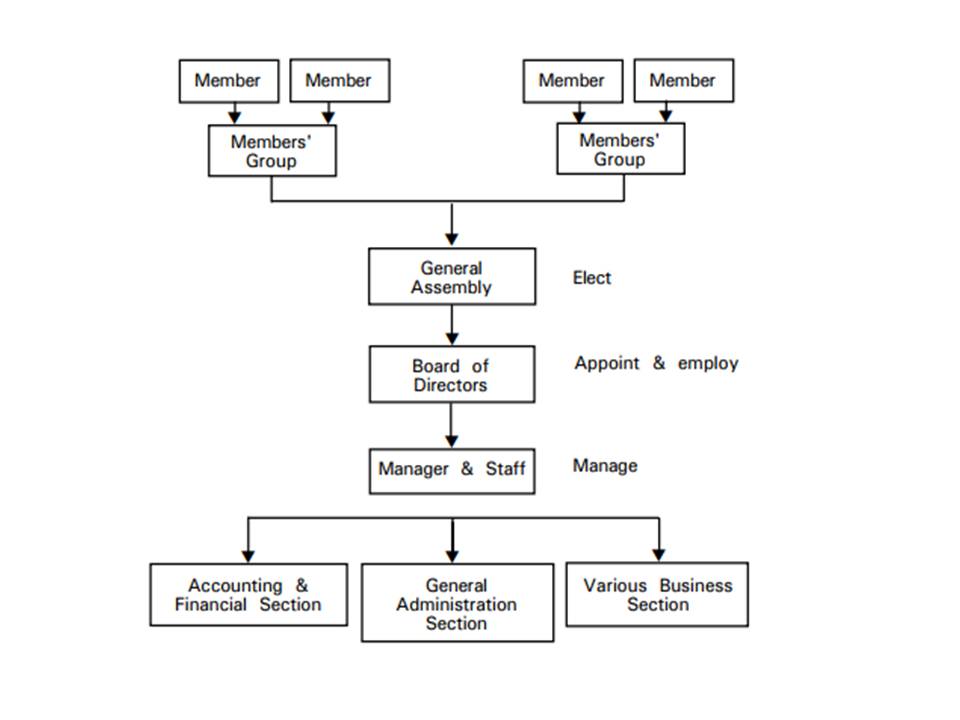
Primary cooperatives at the district level are the foundation of the cooperative movement. They consist of individual members who are divided into groups at the village level. Members are directly involved in the affairs of the cooperative. Usually, the general assembly consists of the total members. According to the present Cooperative Act, the general assembly of members will elect the board of directors (BOD) with a maximum number of not greater than 15 persons with a two-year term. The BOD formulates the policy of the cooperative, and appoints a manager and staff to run the business of the cooperative (Fig.1)

Business Scope and Performances:
Business activities and scopes of agricultural cooperatives.
In order to achieve the economic and social interest of the members, agricultural cooperatives carry out various activities such as:
1) Provide production and consumption loans to members at reasonable rate of interest;
2) Encourage savings among members by promoting savings deposits;
3) Provide agricultural equipment such as tractors, water pumps, and agricultural inputs such as fertilizer, seeds as well as consumption goods to members at reasonable prices; and
4) Assist members to market their products at good prices and to maintain fairness in terms of weight and measurement.
Agricultural cooperatives engage in a wide range of business activities in responding to their members’ needs. Their main business may differ from one area to another but they are mostly involved in four businesses which are credit business, savings and deposit, marketing business, and purchasing business.
1. Credit Business
One of the main functions of agricultural cooperatives is to provide credit facilities to their members. Credit facilities provided by cooperatives cover a variety of activities, such as paddy farming, animal husbandry, debt redemption, and household consumption. The sources of funds for agricultural cooperatives are their own capital (share capital), deposit from members, and loans from financial institutions especially the Bank for Agriculture and Agricultural Cooperative (BAAC) and onward lending to their members for short-, medium-, and long-term periods. The short-term loans are only for emergency needs with a repayment period of two months. The medium-term loans are given for cultivation expenses, including purchase of fertilizers, and for other expenses during planting and harvesting. The repayment period of medium-term loans is 18 months. The long-term loans are given for the purpose of purchase of agricultural equipment, building or repairing houses, purchase of property especially land, and also repaying debts. The period of repayment is more than five years.
2. Savings and Deposit Business
Agricultural cooperatives promote savings among members. Savings can also be used to invest and generate profit to both cooperatives and their members. Members of agricultural cooperatives can open Savings Deposit accounts, Special Savings Deposit accounts, or Fixed Deposit accounts with their cooperatives. They are encouraged to deposit a part of the income they receive from selling their produce to the cooperatives in their accounts.
3. Marketing Business:
One of the important activities of agricultural cooperatives is marketing of agricultural products especially those produced by the members. Farmer-members can obtain good prices, while fair weights and measures are guaranteed. In some agricultural cooperatives, food processing such as milled rice and canned fruits were introduced to generate more income for their members. Some have also become centers for marketing of members’ products.
4. Purchasing Business:
The business of selling major agricultural inputs such as fertilizer, seeds, gasoline etc., and farm supplies and equipment also benefits members because it reduces production costs as well as household expenses. Farmers are assured of fair prices when they buy through cooperatives.
Type of Agricultural Cooperatives
Agricultural cooperatives are generally organized among the people engaging in agricultural earning with varying kinds and degrees of need, thus resulting with various agricultural cooperative types. Besides the general agricultural cooperatives, there are some special types of agricultural cooperative such as:
- Water Users Cooperatives. Members of the cooperative type are farmers living in the same area along a canal or other water source which they jointly use. Joint utilization and maintenance of this valuable resource is the main purpose of this cooperative type.
- Land Reform Cooperatives. This cooperative type is established as part of the government’s land reform program in land reform areas. The main purpose is to assist farmer members in agricultural production as well as to enable them gaining access to capital, agricultural necessities, marketing, saving facilitating and improving members’ lining condition.
- Special Cooperatives. This is formed among farmers who raise animals such as cattle, swine, etc. Joint marketing of these products enables members to obtain good prices and fairness in trading. Dairy cooperatives are among these. They either process milk for sale in the general marker or sell raw milk to private firms producing dairy products.
- National Security Command Cooperatives. This cooperative type has been initiated by the Supreme Command to help people in remote areas improving their living conditions through productive occupation promotion.
- Rubber Cooperatives. Rubber Cooperatives are organized among rubber planters. Through their cooperatives, the members share various aspects of rubber production and marketing , including product development , processing and managing of the cooperative business.
- Cooperatives in the Border Patrol Police School. This special cooperative type is under the auspices of Her Royal Highness Princess Maha Chakri Sirindhorn who believes in cooperative method of self-help and mutual help and mutual help which would provide the youth with a meaningful ways of future living.

















